
Overall, older adults are most disadvantaged when tests use explicit memory, in particular episodic memory, compared to younger adults. Recognition requires less cognitive effort because a target or cue is provided as a prompt to aid recall, as opposed to a recall task, which requires an individual to recall the material to which she or he was previously exposed, without any prompt. 6 Compared to younger adults, older adults typically perform better on recognition tasks as opposed to recall tasks.
#EXPLICIT MEMORY TRIAL#
Most memory tests assess episodic memory and usually involve a free recall (retrieval), cued recall, and recognition trial and rely on an individual's ability to recollect the material to which he or she was previously exposed.

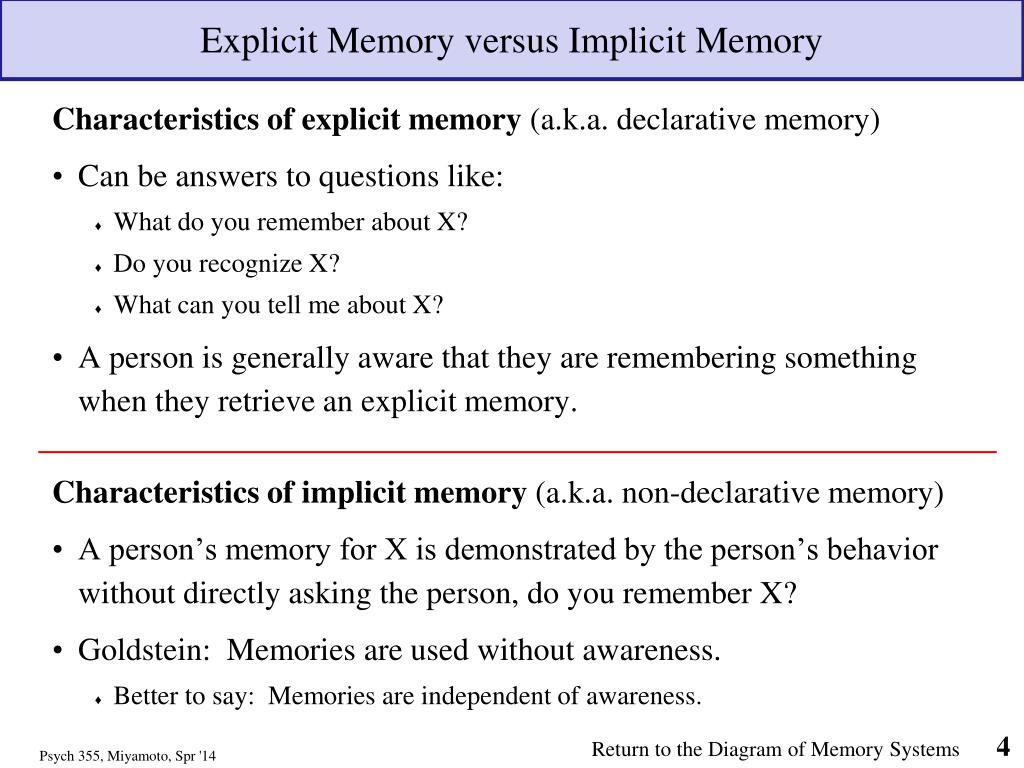
These are memories that relate to an individual's own unique experience and include the details of “when and where” an event occurred. Episodic material includes autobiographical information, such as the birth of a child or graduation from high school, and includes personal information, such as a meal from the previous day or a recent golf game. 34 More specifically, episodic memory is the conscious recollection of personal events, along with the specific time and place (context) that they occurred. Episodic memory refers to the ability to recollect everyday experiences. Fillit MD, in Brocklehurst's Textbook of Geriatric Medicine and Gerontology, 2017 Explicit Memory.Įxplicit memory, often referred to as declarative memory, can further be divided into episodic memory and semantic memory.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
